Prosthetics have been around for centuries, but the advancements in biomedical engineering have transformed the way we think about them. Prosthetics have evolved from simple wooden or metal limbs to complex bionic systems that can restore the abilities of amputees and even enhance human capabilities. With the rapid development of technology, the future of prosthetics in biomedical engineering is promising.
Prosthetics have traditionally been viewed as a tool for restoring lost function, such as the ability to walk or grasp objects. However, with the advancements in technology, prosthetics can now go beyond just restoring function. Prosthetic limbs can be designed to provide sensory feedback, such as touch or temperature, which can greatly enhance the user’s experience. Additionally, prosthetics can be designed to work seamlessly with the human body, allowing for a more natural range of motion and increased comfort.
“Biomedical engineering is not just about building better prosthetics. It’s about restoring lives and redefining what’s possible.”
Robert Lange
Significant Advancements in Prosthetics
One of the most significant advancements in prosthetics is the use of neural interfaces. A neural interface is a device that connects the nervous system to an external device, such as a prosthetic limb. This allows the user to control the prosthetic limb using their thoughts. In recent years, there have been numerous breakthroughs in this area, and researchers are optimistic about the potential of neural interfaces in prosthetics.
Another area of development in prosthetics is the use of 3D printing. 3D printing allows for the production of prosthetics that are customized to the user’s body, which can greatly improve comfort and functionality. Additionally, 3D printing has the potential to reduce the cost of prosthetics and make them more accessible to those who need them.

Advancements in materials science have also had a significant impact on prosthetics. For example, researchers are experimenting with using carbon fiber to create prosthetic limbs that are lighter, stronger, and more durable than traditional prosthetics. Additionally, researchers are exploring the use of smart materials, such as shape-memory alloys, that can change shape in response to different stimuli. This could allow for prosthetic limbs that are more adaptable and responsive to the user’s needs.
- Improves skills
- Gives free time
- Makes you more active
- Relieves fatigue
As technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for prosthetics in biomedical engineering are endless. In the future, we may see prosthetic limbs that are indistinguishable from natural limbs, with the ability to sense touch and temperature, and provide a full range of motion. Additionally, advancements in neural interfaces may allow for the development of prosthetic limbs that can be controlled with the user’s thoughts, making them feel even more like a natural part of the body.
Facts About Technologies
The future of prosthetics in biomedical engineering is bright, and it is an exciting time to be involved in this field. With continued research and development, prosthetics have the potential to transform the lives of amputees and those with mobility impairments, allowing them to regain their independence and improve their quality of life.
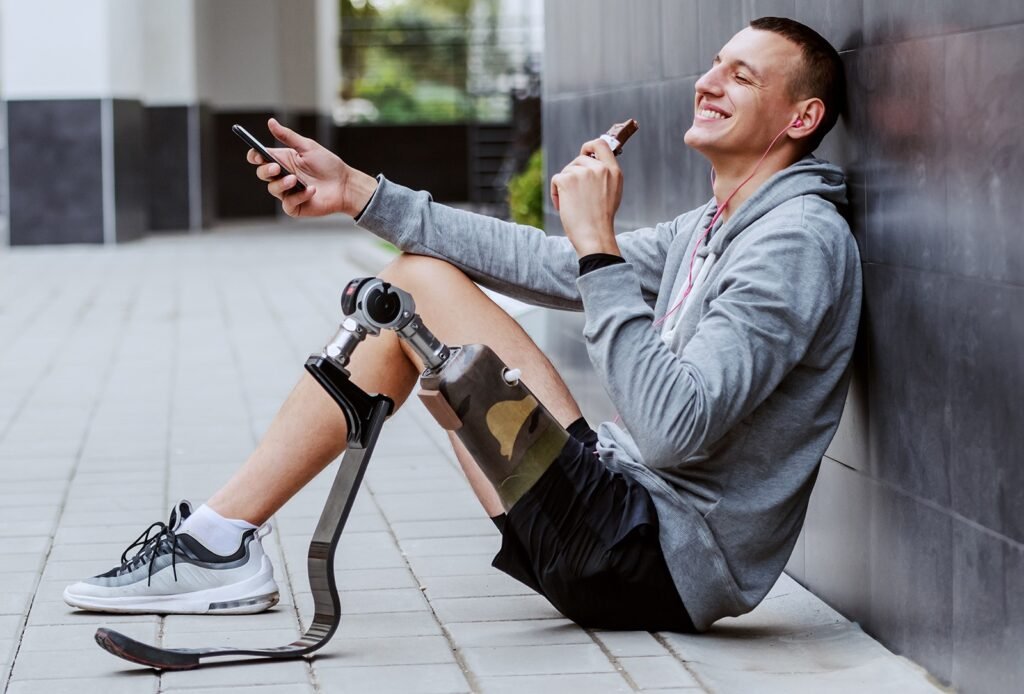

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a rapidly growing field that has the potential to revolutionize many industries, including biomedical engineering. In the field of prosthetics, AI is being used to develop advanced systems that can enhance the functionality and effectiveness of prosthetic devices. In this article, we will discuss the ways in which AI is being used in prosthetics.
One of the most significant ways in which AI is being used in prosthetics is in the development of neural interfaces. A neural interface is a device that connects the nervous system to an external device, such as a prosthetic limb. This allows the user to control the prosthetic limb using their thoughts. AI algorithms are being used to interpret the signals from the neural interface, allowing for more precise control of the prosthetic limb. This can lead to more natural and fluid movements, which can greatly improve the user’s quality of life.
Different Types of Prosthetics
Another way in which AI is being used in prosthetics is in the development of prosthetic control systems. AI algorithms are being used to analyze and interpret data from sensors on the prosthetic device, such as force sensors, gyroscopes, and accelerometers. This data is then used to control the movement of the prosthetic limb in real-time, allowing for more responsive and adaptive movements.
AI is also being used to develop prosthetic devices that can learn from the user’s behavior and adapt to their needs. For example, an AI algorithm can analyze the user’s gait and make adjustments to the prosthetic device to improve their walking ability. Additionally, AI algorithms can learn from the user’s movements and adapt the prosthetic device to better match their preferences and habits.



One of the most promising applications of AI in prosthetics is in the development of smart prosthetic devices. Smart prosthetics are devices that can communicate with the user and adapt to their needs in real-time. AI algorithms can be used to analyze data from the prosthetic device and provide feedback to the user, such as alerts when the prosthetic device needs to be adjusted or repaired.

In conclusion, AI is a rapidly developing field that has the potential to revolutionize the field of prosthetics. AI is being used to develop advanced prosthetic devices that can provide more natural and fluid movements, adapt to the user’s needs, and communicate with the user in real-time. As AI technology continues to evolve, the possibilities for prosthetics in biomedical engineering are endless. With continued research and development, AI has the potential to transform the lives of amputees and those with mobility impairments, allowing them to regain their independence and improve their quality of life.